Table of Contents
Understanding Labor Law in Qatar: Rights, Contracts, Leave, and Legal Remedies for Workers
Labor law in Qatar plays a crucial role in regulating the relationship between employers and employees, ensuring fairness, safety, and protection for all workers, including nationals and expatriates. Whether you're working in a corporate office, managing domestic help, or running a business, knowing the essentials of Qatar's labor law is critical to maintaining legal compliance and safeguarding rights.
Overview of Qatar Labor Law
Qatar's labor law is governed by Law No. 14 of 2004, which covers most employment relationships in the private sector. The law has undergone several amendments, especially with reforms targeting the sponsorship (Kafala) system and enhancing worker protections. Recent updates in 2025 introduced more flexible job mobility and better dispute resolution mechanisms.
The legislation applies to all workers except domestic helpers, public sector employees, and certain sectors governed by special laws. However, the Ministry of Labour has issued specific regulations addressing the rights of domestic workers.
Worker Rights Under Qatar Labor Law
Qatar's labor law grants a variety of rights to employees to ensure a safe and just working environment, as shown in the figure below: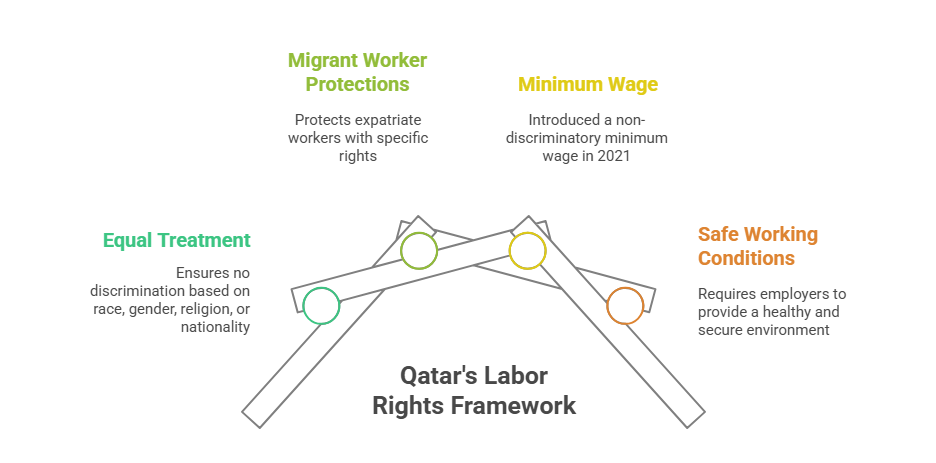
Contracts and Employment Terms
Employment contracts are the cornerstone of the employment relationship. Qatar recognizes two types of contracts:
-
Fixed-term contracts: These run for a specified duration. Termination before the end of the term may incur penalties.
-
Unlimited contracts: These are more flexible but still require proper notice for termination.
Key Employment Terms
-
Probation period: Cannot exceed 6 months.
-
Notice period: Typically one month, extendable up to two months depending on the contract.
-
Termination: Both employers and employees must follow due process. Wrongful termination can lead to compensation.
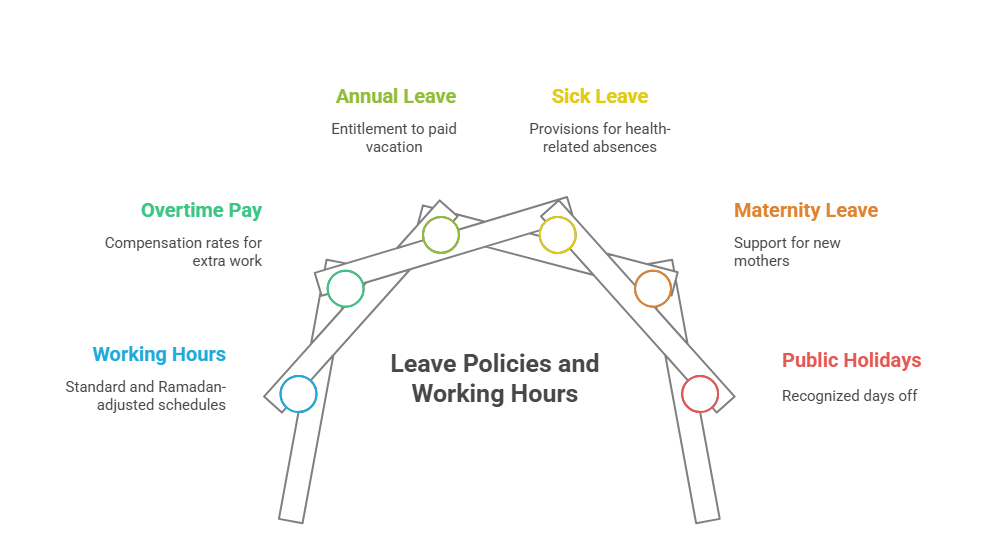
Leave Policies and Working Hours
Qatar labor law ensures various forms of leave and limits on working hours. We can see in the below pict
End of Service and Gratuity
When employment ends, workers are entitled to certain benefits:
-
Gratuity: Workers are eligible for end-of-service gratuity after one year of continuous service. It equals at least three weeks' wages for every year served.
-
Final settlement: Includes all due salary, unused leave compensation, and gratuity.
-
Notice period compensation: If either party fails to honor the notice period, they must pay an equivalent amount in lieu.
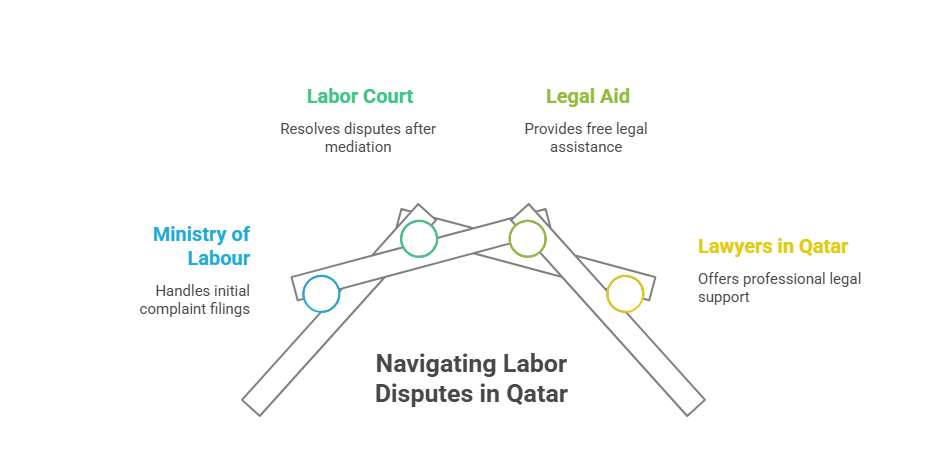
Legal Remedies and Labor Disputes
Dispute resolution is streamlined under Qatar's labor system:
Sponsorship and Visa Transfers
The government has reformed the traditional Kafala system to improve job mobility:
-
Job change: Workers can switch jobs without employer consent after completing their contract or probation.
-
Visa transfer: Permitted under new rules without requiring a No Objection Certificate (NOC).
-
Exit permits: Most workers no longer need employer permission to leave the country.
-
Kafala system reform: The emphasis is now on contractual rather than personal employer-employee ties.
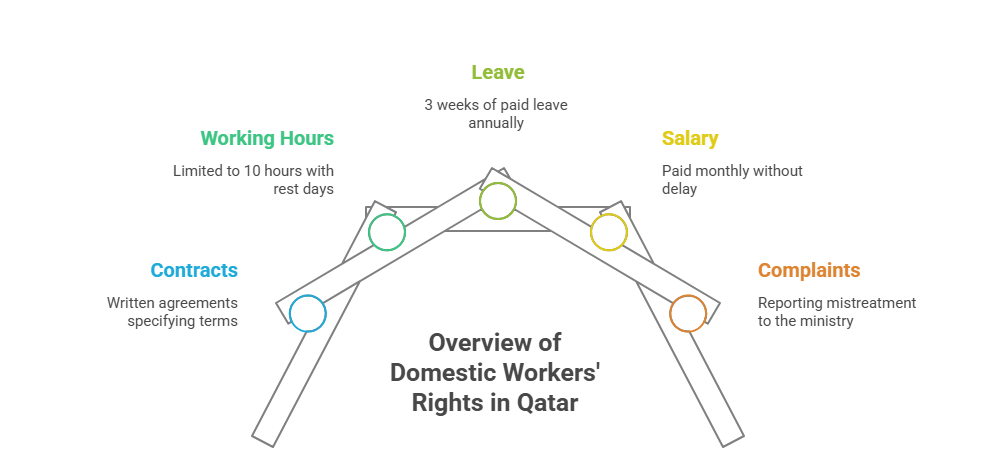
Domestic Workers' Rights
Domestic workers in Qatar are governed by Law No. 15 of 2017, offering a dedicated legal framework:
Conclusion
Qatar has made substantial progress in modernizing its labor laws, aligning them with international labor standards. Workers—whether local, expat, or domestic- now have greater legal protection, clarity in contracts, and accessible routes to justice.
If you are navigating labor-related legal challenges in Qatar, whether as an employer or employee, connecting with a qualified labor lawyer is essential. Visit Lawyers 974 to find trusted labor law experts who can guide you through Qatar’s legal landscape and ensure your rights are fully protected.
Disclaimer: This article provides general information and should not be construed as legal advice. Please consult with a qualified and experienced lawyer for personalized guidance regarding your specific situation.